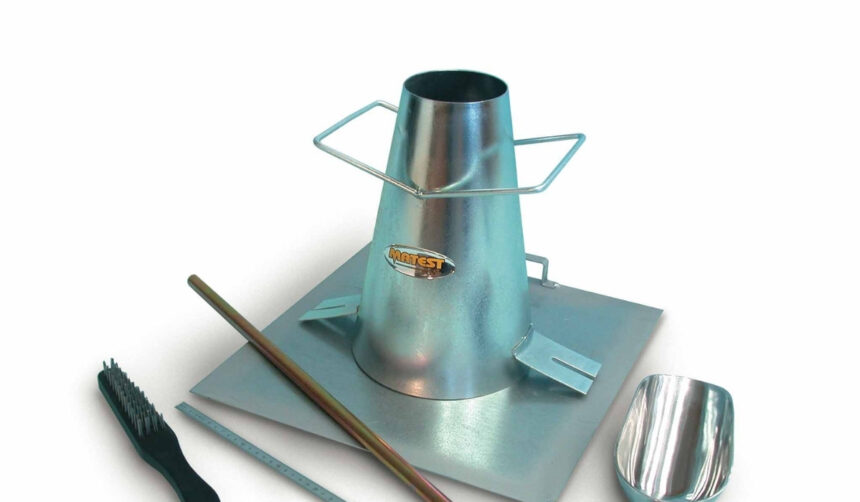
The slump test for concrete is one of the most commonly used methods to assess the workability, consistency, and fluidity of fresh concrete before it sets. Understanding what is the slump test for concrete is critical for engineers, contractors, and construction professionals to ensure the quality and performance of concrete in structural applications. The test is simple, cost-effective, and provides immediate results on-site, allowing for adjustments in the mix design or water content. The primary purpose of the slump test is to verify that the concrete mix has the desired consistency for proper placement, compaction, and finishing, preventing issues such as segregation, honeycombing, or uneven strength distribution.
Purpose and Importance of the Slump Test
Knowing what is the slump test for concrete helps construction professionals maintain the balance between workability and strength. Concrete that is too stiff may be difficult to pour and compact, which can compromise structural integrity. Conversely, overly fluid concrete can result in segregation of aggregates and increased water-cement ratio, reducing durability. The slump test provides a standardized way to measure consistency and ensures that the mix conforms to project specifications. It is a vital quality control measure in construction, particularly in large-scale projects where consistency across batches is crucial for uniform performance.
Equipment Required for the Slump Test
The slump test for concrete requires specific equipment to ensure accuracy and reliability. The standard tools include a slump cone, a tamping rod, a base plate, and a measuring scale. The slump cone is typically a hollow, frustum-shaped metal mold with precise dimensions. The tamping rod is used to compact each layer of concrete inside the cone, ensuring uniform density. The base plate provides a stable surface, and a scale or measuring device is used to determine the vertical displacement of the concrete after the cone is removed. Proper use of this equipment is essential to achieve consistent and repeatable results in understanding what is the slump test for concrete.
Procedure for Conducting the Slump Test
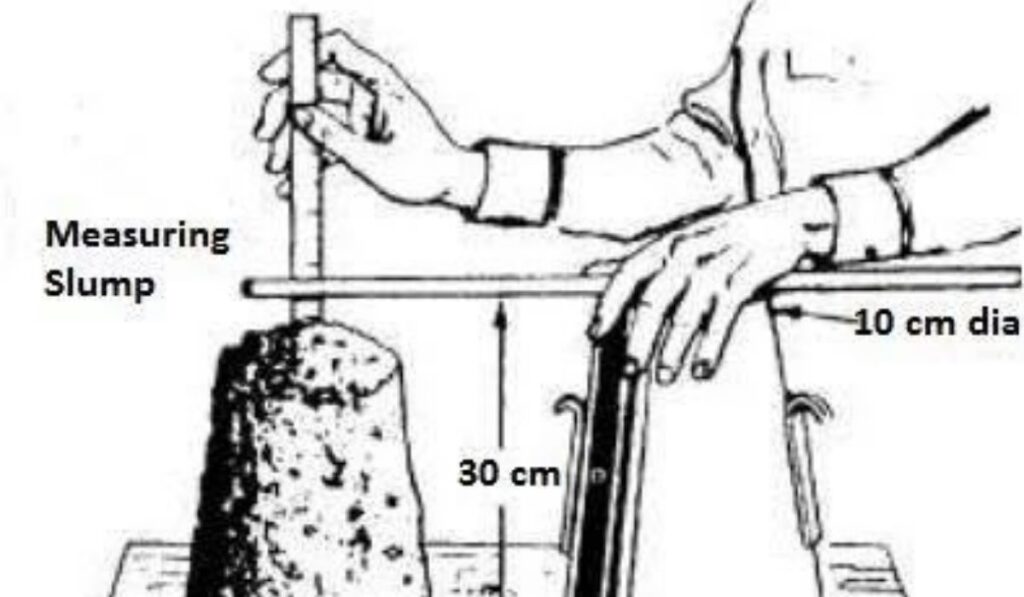
To understand what is the slump test for concrete, it is important to follow the standard procedure accurately. First, the slump cone is placed on a flat, non-absorbent surface and held firmly at its base. Fresh concrete is filled into the cone in three layers, each layer being tamped 25 times with the rod to ensure proper compaction. Once the cone is fully filled and leveled at the top, it is carefully lifted vertically, allowing the concrete to settle freely. The resulting change in height, measured from the original top of the cone to the top of the settled concrete, is called the slump. The measured slump indicates the workability and consistency of the mix.
Types of Slump in Concrete
The slump test for concrete can produce three main types of slumps, each indicating different characteristics of the mix. A true slump occurs when the concrete settles evenly without collapsing, representing a workable mix suitable for most construction purposes. A shear slump occurs when one side of the concrete shears off, indicating uneven mix or cohesion issues. A collapse slump, where the concrete completely collapses, indicates excessive water or high workability, which may not be suitable for structural applications. Understanding what is the slump test for concrete includes recognizing these slump types to make informed decisions about mix adjustments.
Factors Affecting Slump Value
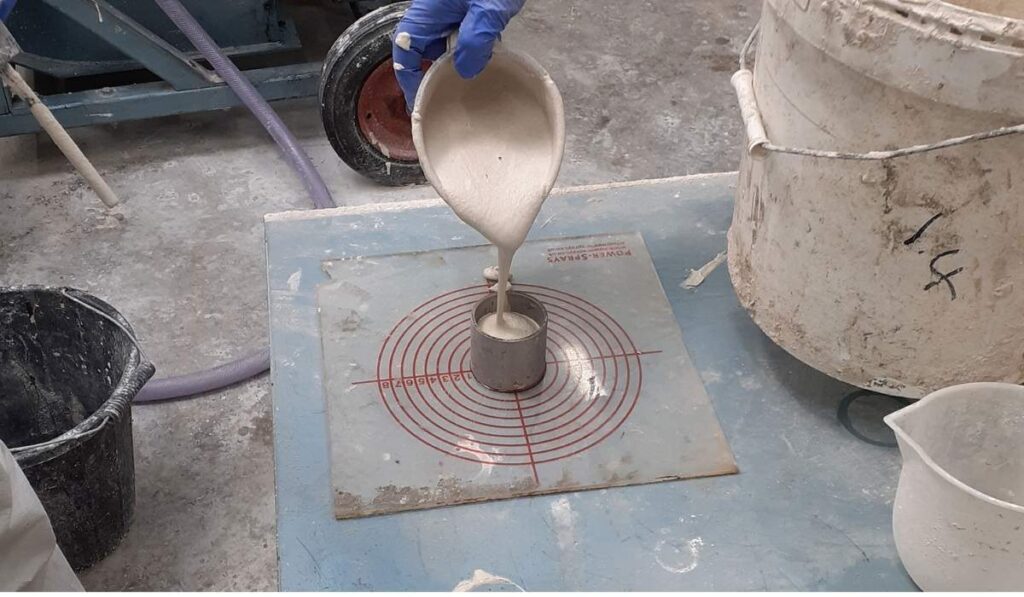

Several factors influence the results of the slump test for concrete, highlighting why it is important to understand what is the slump test for concrete. Water content is the most significant factor; higher water content increases slump, making the concrete more fluid. Aggregate size and grading also affect slump, as larger aggregates reduce workability. Admixtures, such as plasticizers or superplasticizers, can increase slump without altering the water-cement ratio. Temperature and mixing time also play a role in concrete behavior during testing. By analyzing these factors, engineers can modify mix designs to achieve optimal workability while maintaining strength.
Interpreting Slump Test Results
Understanding what is the slump test for concrete involves interpreting the measured slump in relation to the type of construction. Slump values are categorized into low, medium, and high ranges depending on the project requirements. Low slump indicates stiff concrete suitable for pavements or heavy structural elements. Medium slump is typical for general-purpose construction, while high slump is used for highly workable concrete, such as in pumped applications or complex forms. Correct interpretation of the slump results ensures the mix is fit for purpose and prevents potential defects caused by inappropriate workability.
Significance in Quality Control
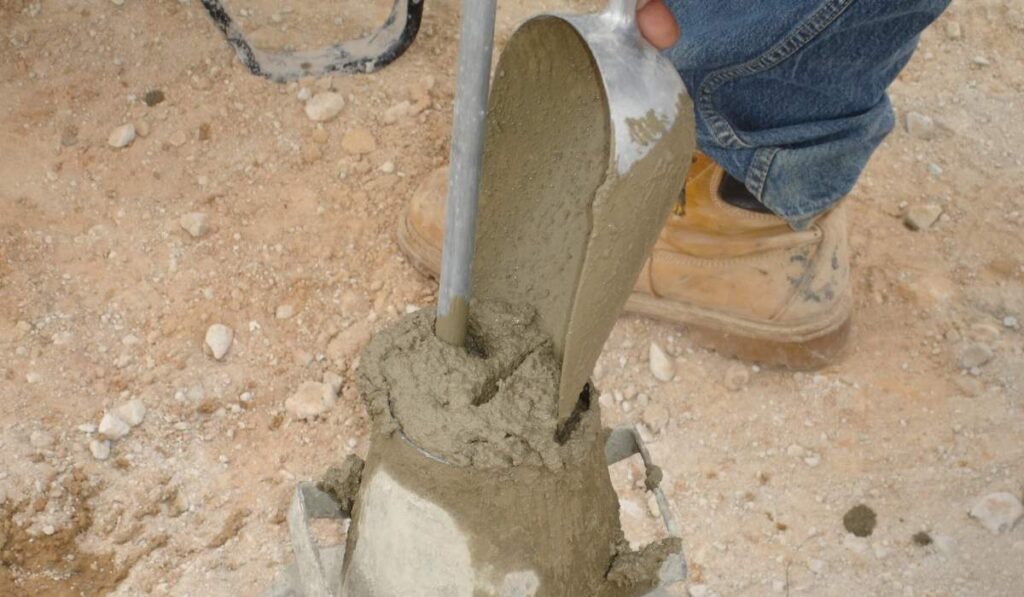

The slump test for concrete is a cornerstone of quality control in construction. By regularly testing batches, contractors can ensure uniformity and consistency, reducing the risk of weak points in structures. Monitoring the slump also helps in verifying that the mix proportions provided by suppliers are accurate and that no excessive water has been added during handling. Understanding what is the slump test for concrete allows project managers to maintain high standards and meet regulatory and design specifications, ultimately contributing to the longevity and safety of concrete structures.
Limitations of the Slump Test
While the slump test for concrete is widely used, it has certain limitations that must be understood. The test provides a measure of workability but does not directly indicate concrete strength. High slump does not guarantee high-quality concrete, as excessive water can weaken the mix. The slump test is also more suitable for normal-weight concrete and may not provide accurate results for lightweight or highly reinforced mixes. Recognizing these limitations is essential for professionals to avoid misinterpretation and to complement slump testing with other quality assessments when determining what is the slump test for concrete.
Conclusion
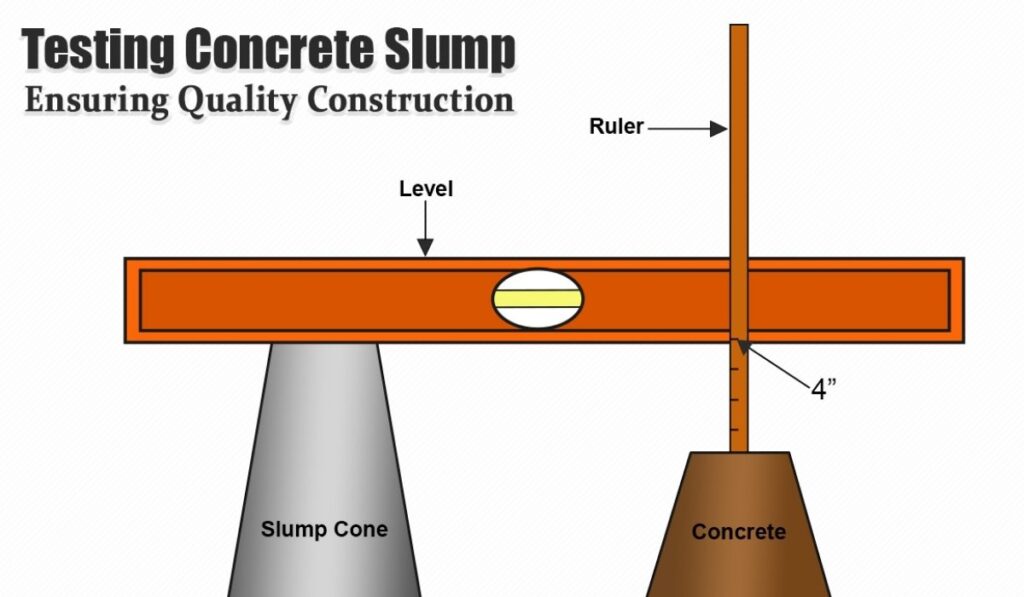
In conclusion, the slump test for concrete is an essential method to assess the consistency and workability of fresh concrete. Understanding what is the slump test for concrete allows engineers and construction professionals to make informed decisions regarding mix design, placement, and compaction. The test is simple, cost-effective, and provides immediate feedback, making it an indispensable tool for quality control in construction. While it has limitations, when used alongside other assessments, it ensures that concrete achieves the desired performance, strength, and durability required for safe and effective structures.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the purpose of the slump test for concrete?
- It measures the workability and consistency of fresh concrete before placement.
2. How is the slump test for concrete performed?
- Concrete is filled in a slump cone in layers, tamped, and then the cone is removed to measure settlement.
3. What types of slump are observed in the slump test?
- True slump, shear slump, and collapse slump indicate different workability levels.
4. What factors affect the slump value of concrete?
- Water content, aggregate size, admixtures, temperature, and mixing time influence slump.
5. Can slump test results predict concrete strength?
- No, it only measures workability and consistency, not the compressive strength.