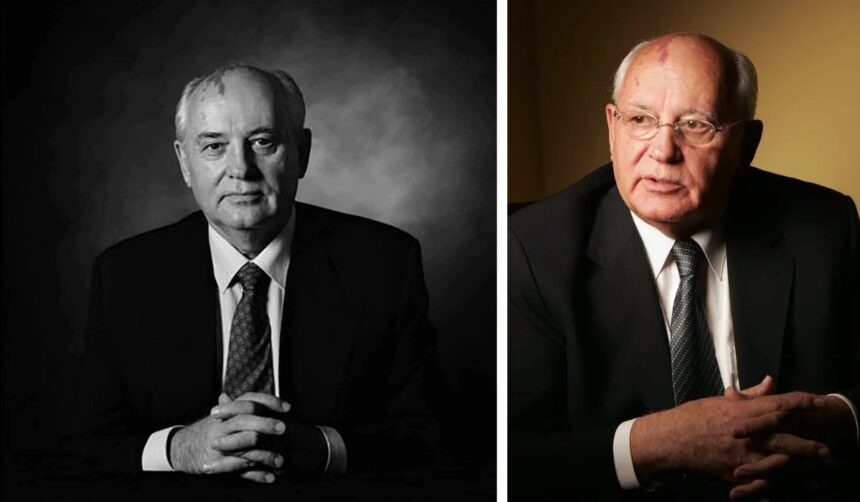
Mikhail Gorbachev is widely regarded as one of the most pivotal figures in modern world history. He is best known as the last leader of the Soviet Union, whose bold reforms helped reshape the political landscape of the 20th century. Gorbachev’s policies of perestroika (restructuring) and glasnost (openness) marked a significant departure from the rigid, authoritarian style of Soviet governance that had dominated for decades. His efforts not only aimed at revitalizing the Soviet economy but also at fostering political transparency and improving international relations.
Gorbachev’s influence extended far beyond the borders of the USSR. He played a central role in easing Cold War tensions, signing key arms control treaties with the United States, and ultimately influencing the peaceful collapse of communist regimes across Eastern Europe. Despite his enormous impact, Gorbachev’s tenure was not without controversy, as his reforms faced resistance from hardliners, and economic difficulties persisted. Nevertheless, his legacy as a reformist and statesman is undeniable.
Quick Bio
| Attribute | Details |
| Full Name | Mikhail Sergeyevich Gorbachev |
| Date of Birth | March 2, 1931 |
| Place of Birth | Privolnoye, Stavropol Krai, Russia |
| Education | Moscow State University, Law |
| Spouse | Raisa Titarenko Gorbachev |
| Children | Irina Mikhailovna Gorbacheva |
| Political Party | Communist Party of the Soviet Union |
| Key Positions | General Secretary of the Communist Party, President of the USSR |
| Major Achievements | Perestroika, Glasnost, Ending Cold War, Nobel Peace Prize 1990 |
| Net Worth | Approx. $2 million |
Early Life and Education
Mikhail Gorbachev was born on March 2, 1931, in the village of Privolnoye, Stavropol Krai, in southern Russia. He grew up in a modest peasant family, where hard work and community values were central to daily life. These early experiences shaped Gorbachev’s worldview, instilling a strong sense of responsibility and a belief in social justice.
As a young man, he pursued higher education in law at Moscow State University, where he joined the Communist Party in 1952. His time in Moscow exposed him to the political and intellectual currents of the era, preparing him for a future role in Soviet governance. Gorbachev demonstrated exceptional organizational and communication skills, which helped him rise steadily through the party ranks.
Political Rise in the Soviet Union
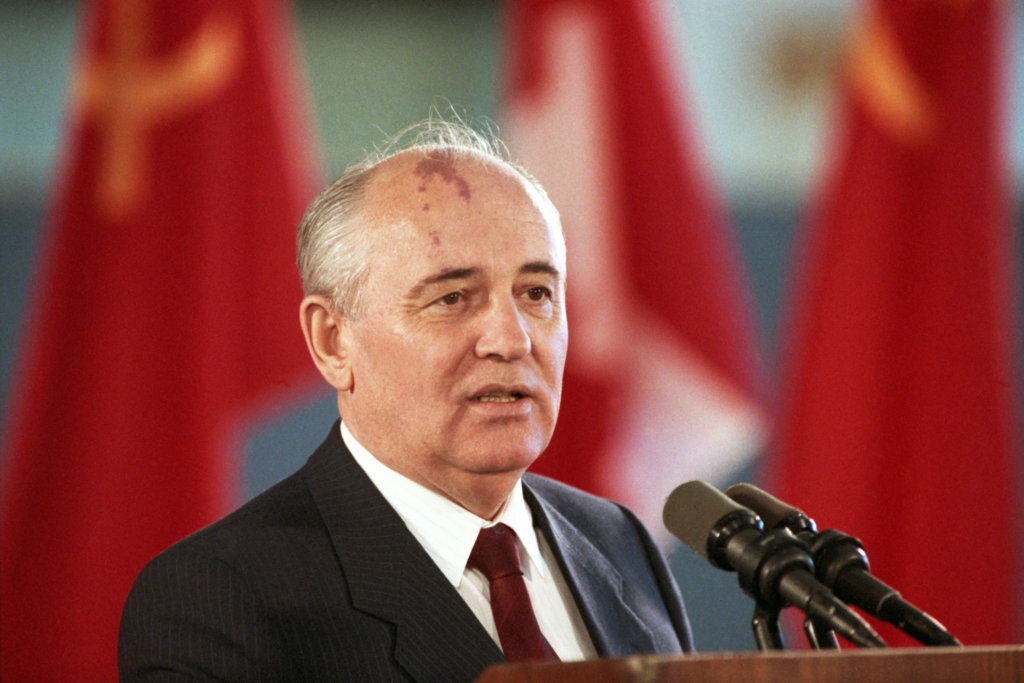

Gorbachev’s political career began in the Stavropol region, where he worked in various party roles, gradually gaining recognition for his efficiency and reform-minded approach. By the 1970s, he had become a prominent figure in the Soviet political apparatus.
In 1985, following the death of Konstantin Chernenko, Gorbachev was elected General Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union. At just 54 years old, he was one of the youngest leaders in decades. His rise marked a generational shift in Soviet politics, as he represented a new breed of leaders who were willing to rethink the status quo.
Perestroika: Economic Restructuring
One of Gorbachev’s most notable initiatives was perestroika, or restructuring, aimed at revitalizing the stagnant Soviet economy. The policy sought to introduce limited market-like reforms, decentralize economic decision-making, and improve efficiency in state-owned enterprises.
While perestroika was ambitious, its implementation faced significant challenges. The centralized Soviet system was resistant to change, and many reforms were only partially enacted. Nonetheless, perestroika marked a dramatic departure from decades of rigid economic control and laid the groundwork for future transitions.
Glasnost: Promoting Openness
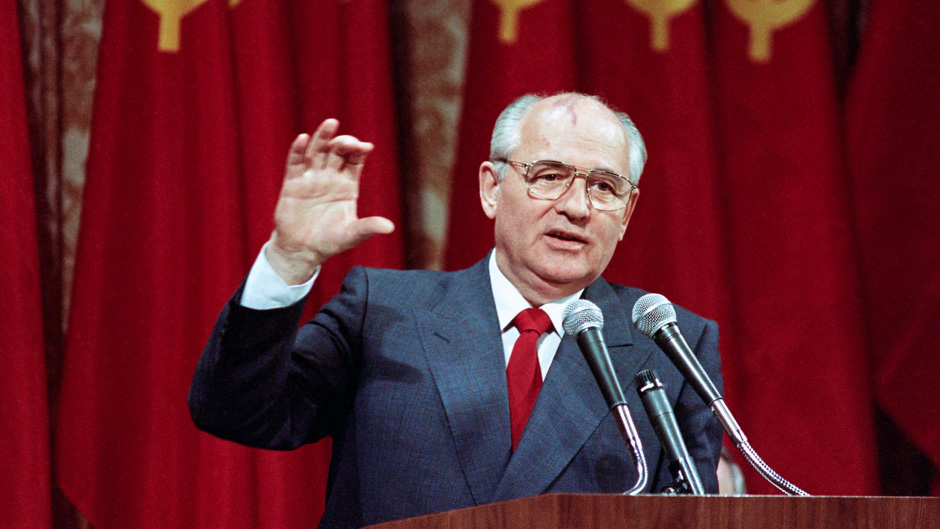

Alongside economic reform, Gorbachev introduced glasnost, a policy designed to increase political transparency and freedom of expression. Glasnost allowed for open discussion of social and political issues, unprecedented media freedom, and a greater role for citizens in governance.
This policy dramatically altered Soviet society. Citizens could criticize government policies, journalists reported more freely, and previously taboo subjects such as historical atrocities and government corruption were openly discussed. While glasnost fostered a more informed and engaged populace, it also exposed deep societal and political fractures, which contributed to the eventual dissolution of the Soviet Union.
Foreign Policy and International Impact
Mikhail Gorbachev’s leadership had a profound impact on international relations. His commitment to reducing Cold War tensions led to landmark agreements with the United States, including the Intermediate-Range Nuclear Forces (INF) Treaty. Gorbachev’s diplomatic approach emphasized dialogue, negotiation, and cooperation rather than confrontation.
He also encouraged Eastern European nations to pursue political reforms, signaling a retreat from strict Soviet control. This policy indirectly facilitated the fall of communist regimes across the region, culminating in events such as the fall of the Berlin Wall. Gorbachev’s approach to foreign policy earned him worldwide recognition and the 1990 Nobel Peace Prize.
Challenges and Criticism

Despite his many achievements, Gorbachev faced substantial criticism both domestically and internationally. Economically, perestroika did not produce immediate improvements, and food shortages and inflation became serious issues. Politically, his reforms angered conservative elements within the Communist Party, leading to tension and ultimately a failed coup attempt in 1991.
Many Russians felt that Gorbachev’s policies weakened the state and undermined national stability. Nevertheless, historians often view his leadership as courageous, as he prioritized reform and peace over maintaining power at all costs.
Personal Life
Mikhail Gorbachev married Raisa Titarenko in 1953, and she played a significant role as his partner throughout his political career. Raisa was known for her intelligence, charisma, and involvement in social programs, making the couple a prominent public image of Soviet leadership. The Gorbachevs had one daughter, Irina, who later became an academic and public figure.
Legacy and Death of the Soviet Union
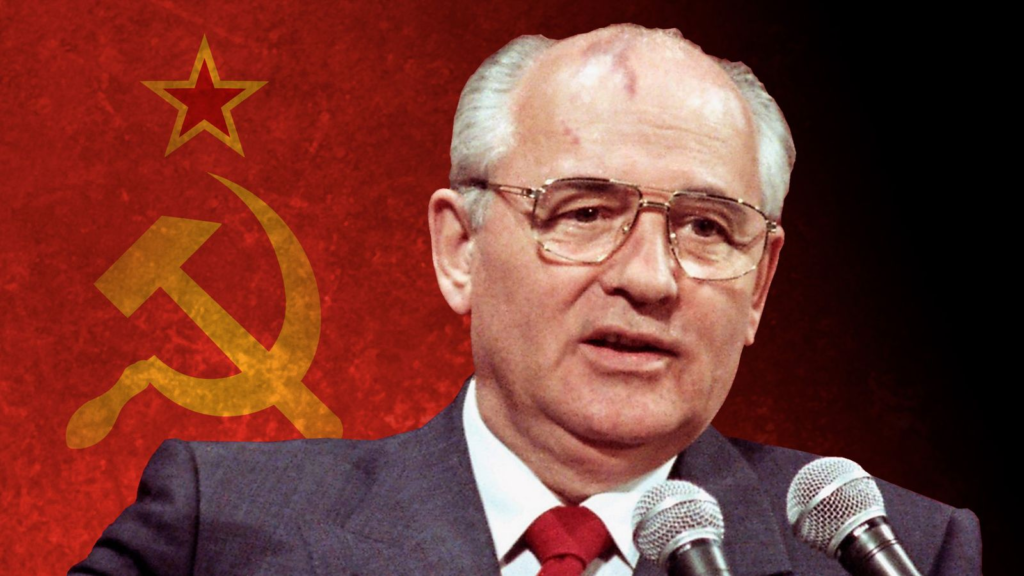

Gorbachev’s legacy is inextricably linked to the collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991. While he sought to reform the system, he ultimately could not prevent its disintegration. Many argue that his policies were visionary and necessary, even if they had unintended consequences.
Today, Gorbachev is remembered for his commitment to peace, openness, and reform. His role in ending the Cold War and transforming global politics remains a major point of historical discussion and analysis.
Mikhail Gorbachev’s Net Worth
Although Mikhail Gorbachev was a head of state, he never amassed significant personal wealth in the way modern political figures sometimes do. His net worth has been estimated at around $2 million, primarily derived from pensions, speaking engagements, and book royalties. Gorbachev remained relatively modest in lifestyle compared to contemporary global leaders, which has contributed to his image as a principled and dedicated public servant.
Awards and Recognitions
Gorbachev received numerous accolades during and after his political career. Among the most notable are the Nobel Peace Prize in 1990, the Order of Merit from Germany, and various international honors recognizing his efforts toward global diplomacy, reform, and nuclear disarmament. His influence is studied in universities worldwide, and his writings continue to provide insights into governance and international relations.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Who was Mikhail Gorbachev?
- Mikhail Gorbachev was the last leader of the Soviet Union, known for implementing reforms such as perestroika and glasnost and playing a crucial role in ending the Cold War.
2. What is perestroika?
- Perestroika was Gorbachev’s policy of economic restructuring aimed at modernizing the Soviet economy through limited market reforms and decentralization.
3. What is glasnost?
- Glasnost, meaning openness, was a policy introduced by Gorbachev to encourage political transparency, freedom of speech, and public discussion of societal issues.
4. What was Gorbachev’s net worth?
- Mikhail Gorbachev’s net worth is estimated to be around $2 million, primarily from pensions, speaking engagements, and book royalties.
5. What is Mikhail Gorbachev’s legacy?
- Gorbachev’s legacy includes ending the Cold War peacefully, initiating political and economic reforms in the USSR, and promoting global diplomacy, transparency, and peace.