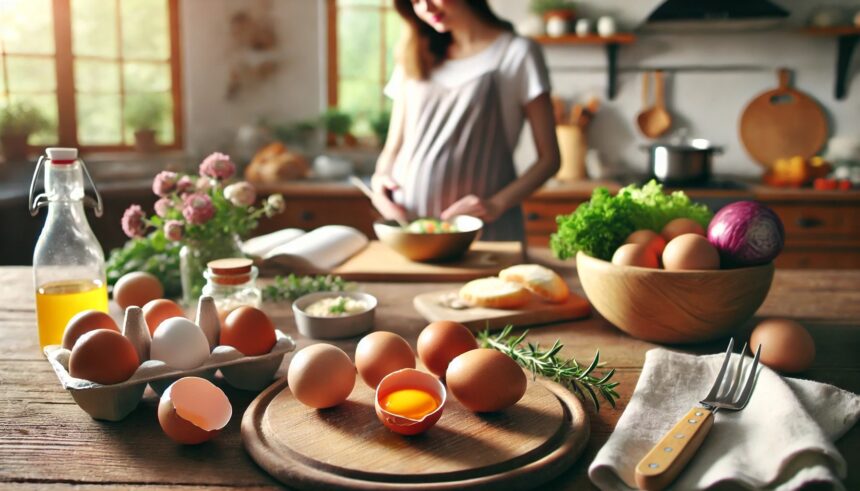
Pregnancy is an exciting time in a woman’s life, but it also comes with a lot of questions and concerns about what to eat and what to avoid. Among these concerns is the question: Can you eat duck eggs during pregnancy? Duck eggs are nutritious and can offer several health benefits, but like any other food, it’s important to know if they are safe to eat during pregnancy.
What Are Duck Eggs?
Duck eggs are a type of egg that comes from female ducks. They are often larger than chicken eggs, with thicker shells and a higher fat content. The yolk of a duck egg is larger and more vibrant in color than a chicken egg yolk.
They are known for their rich, creamy texture and are a popular choice in many cultures around the world. Duck eggs are commonly used in baking, cooking, and traditional dishes.
Duck eggs are considered to be more nutritious than chicken eggs. They contain more protein, fat, and other vitamins and minerals, including vitamin A, B vitamins, iron, and calcium. Despite their nutritional value, the question of whether it is safe to consume duck eggs during pregnancy arises because of the risk of foodborne illnesses.
Are Duck Eggs Safe During Pregnancy?
The answer to this question is generally yes, duck eggs can be safe to eat during pregnancy, but with some important precautions.
1. Avoid Raw Duck Eggs
Like chicken eggs, duck eggs can carry harmful bacteria such as Salmonella, which can cause food poisoning. During pregnancy, foodborne illnesses can be more severe, affecting both the mother and the baby. To reduce the risk of infection, pregnant women should avoid consuming raw or under-cooked duck eggs, such as in dishes like homemade mayonnaise, eggnog, or sushi.
2. Cook Duck Eggs Properly
The best way to ensure that duck eggs are safe to eat during pregnancy is to cook them thoroughly. Cooking eggs to a temperature of 160°F (71°C) kills harmful bacteria. You can safely enjoy duck eggs if they are fully cooked, whether they are scrambled, fried, boiled, or baked.
3. Ensure Freshness
When purchasing duck eggs, ensure that they are fresh and have been stored properly. Duck eggs should be kept in a cool place and used within their recommended shelf life. It’s always a good idea to buy eggs from a trusted source, especially during pregnancy when food safety is more important.
4. Check for Cracks
Before eating any eggs, check for cracks in the shell. Cracked eggs are more likely to harbor bacteria, so it’s best to discard any eggs with damaged shells.
Health Benefits of Eating Duck Eggs During Pregnancy
Duck eggs can offer many health benefits, especially for pregnant women. They are packed with nutrients that can support both the mother and the baby’s health. Here are some of the key benefits of duck eggs during pregnancy:
1. Rich in Protein
Duck eggs are an excellent source of protein, which is crucial for building and repairing tissues during pregnancy. Protein also helps in the growth and development of the baby, including the development of muscles, tissues, and organs.
2. High in Vitamins and Minerals
Duck eggs are rich in essential vitamins and minerals, including:
Vitamin A: Supports healthy vision and immune function.
B Vitamins: Important for the production of red blood cells and energy.
Iron: Helps prevent iron-deficiency anemia, which is common during pregnancy.
Calcium: Necessary for developing strong bones and teeth in the growing baby.
3. Healthy Fats
Duck eggs have higher fat content than chicken eggs, which can help meet the increased calorie needs during pregnancy. Healthy fats are important for the development of the baby’s brain and nervous system.
4. Choline for Brain Development
Duck eggs are also a good source of choline, a nutrient that plays a key role in brain development and fetal memory. Adequate choline intake during pregnancy can help ensure proper neural tube development in the baby.
Nutritional Comparison: Duck Eggs vs Chicken Eggs
To better understand the nutritional value of duck eggs, here’s a comparison between duck and chicken eggs:
| Nutrient | Duck Egg (1 large) | Chicken Egg (1 large) |
| Calories | 130-150 kcal | 70-80 kcal |
| Protein | 9-13 grams | 6-7 grams |
| Fat | 9-12 grams | 5 grams |
| Cholesterol | 620 mg | 185 mg |
| Vitamin A | 300 IU | 270 IU |
| Iron | 1.2 mg | 0.9 mg |
| Calcium | 60 mg | 28 mg |
| Choline | 140 mg | 125 mg |
As you can see, duck eggs have more calories, fat, and protein compared to chicken eggs. This makes them an excellent option for pregnant women who need extra energy and nutrients. However, the higher cholesterol content of duck eggs may be a concern for some people, especially those with cholesterol issues, but for most people, it’s not a major issue when eaten in moderation.
Risks of Eating Duck Eggs During Pregnancy
While duck eggs can provide numerous health benefits, there are also potential risks that pregnant women should be aware of.
1. Risk of Salmonella
As mentioned earlier, duck eggs can be contaminated with Salmonella bacteria. This bacteria can lead to food poisoning and cause symptoms like nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea, and fever. If left untreated, food poisoning can be harmful to both the mother and the baby. Always cook duck eggs properly to kill any harmful bacteria.
2. Allergic Reactions
Some people may be allergic to duck eggs, just as they might be allergic to chicken eggs. If you are allergic to chicken eggs, you may also have an allergic reaction to duck eggs. Symptoms of an allergy include skin rashes, swelling, difficulty breathing, and stomach upset. If you experience any of these symptoms, seek medical attention immediately.
3. High Cholesterol
Duck eggs are higher in cholesterol than chicken eggs. While moderate consumption is generally fine for most people, those with high cholesterol or heart disease may want to limit their intake of duck eggs.
FAQs
1. What do duck eggs taste like?
Duck eggs have a richer, more intense flavor compared to chicken eggs, with a creamier yolk and firmer whites.
2. How do duck eggs compare to chicken eggs nutritionally?
Duck eggs are larger and contain more protein, fat, vitamins A, B12, D, and omega-3 fatty acids than chicken eggs.
3. Can people allergic to chicken eggs eat duck eggs?
Some individuals allergic to chicken eggs can consume duck eggs without issues, as they contain different proteins. However, caution is advised, and it’s best to consult with an allergist.
4. How should duck eggs be stored?
Unwashed duck eggs can be stored at room temperature for about three weeks due to their thicker shells. Refrigeration extends their shelf life to several months.
5. Are duck eggs safe to eat raw?
Consuming raw duck eggs carries a higher risk of foodborne illnesses, such as salmonella. It’s recommended to cook them thoroughly before consumption.
6. How do you cook duck eggs?
Duck eggs can be cooked like chicken eggs, scrambled, fried, boiled, or poached. Due to their higher fat content, they may cook faster, so watch them closely.
7. Why are duck eggs more expensive than chicken eggs?
Duck eggs are larger and ducks require more food and care, contributing to higher production costs, which makes them more expensive than chicken eggs.
8. How can I incorporate duck eggs into my diet?
Duck eggs can replace chicken eggs in most recipes, enhancing the richness of dishes like omelets, baking, and custards.
9. Do duck eggs need to be washed before storing?
It’s best not to wash duck eggs immediately, as they have a natural protective coating called the “bloom.” If washing is necessary due to dirt, use warm water and dry them thoroughly before storing.
10. Can duck eggs be used in baking?
Yes, duck eggs are excellent for baking, providing richer flavor and fluffier textures in cakes, breads, and other baked goods.
11. Do ducks lay eggs every day?
Many duck breeds lay eggs almost daily, with some breeds laying up to 340 eggs per year.
12. How can I tell if a duck egg is fertilized?
Fertilized duck eggs develop a small white spot on the yolk called a blastoderm, while unfertilized eggs have a blastodisc, which appears as a circular white spot.
13. Are duck eggs suitable for people with cholesterol concerns?
Duck eggs contain higher cholesterol levels than chicken eggs. Individuals with cholesterol concerns should consume them in moderation and consult with a healthcare provider.
14. How long does it take for duck eggs to hatch?
On average, duck eggs take about 28 days to hatch under proper incubation conditions.
15. Do duck eggs require special handling during incubation?
Yes, duck eggs have specific temperature and humidity requirements during incubation. Maintaining a consistent temperature of 99.5°F and appropriate humidity levels is crucial for successful hatching.